Cataract Treatment in Vileparle and Santacruz
Cataract Diagnosis & Treatment


Best Pediatric Ophthalmologist In Mumbai
What is Pediatric Ophthalmology?
The distinction between the visual system of a child and an adult arises from the ongoing maturation process in the child’s eye, which is crucial for optimal vision and the effective communication between the eye and the brain. Consequently, any issues impacting a child’s visual health necessitate prompt intervention due to the critical nature of early treatment. This necessity has led to the establishment of pediatric ophthalmology as an independent specialized field.

Pediatric Ophthalmology Symptom Checker
- Viewing TV from too close
- Difficulty in copying from the blackboard
- Stumbling or tripping while walking
- Reading books very close to face
- Deviation of eyes
- Unusual head position
- Shaking of eyes
- White reflex in the centre of eyes
- Itching
- Bulging of eyes








Major Children Eye Diseases

Refractive Errors
Refractive errors are not diseases but rather eye conditions. They encompass myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism. Myopia, or nearsightedness, allows clear vision of nearby objects but blurs distant ones.
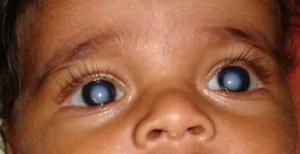
Pediatric Cataract
Cataract refers to any clouding of the eye’s lens, leading to decreased vision. In children, cataracts can be present from birth or develop later. They can affect one or both eyes and are generally treatable.

Squint or Strabismus
Squint is when the eyes aren’t aligned and point in various directions. One eye might turn in, out, up, or down. It can happen in childhood or adulthood, but there are distinctions between squint in kids and adults.
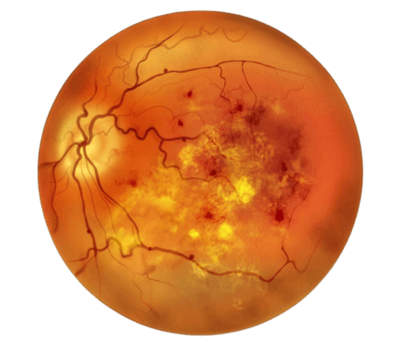
Diabetic Retinopathy
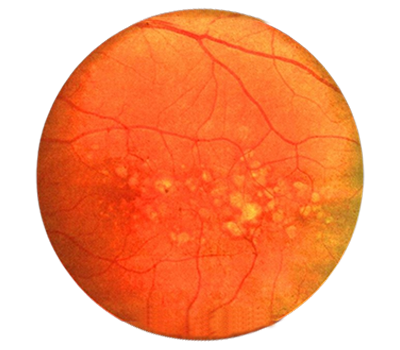
Age-related macular degeneration

Retinal vein occlusion
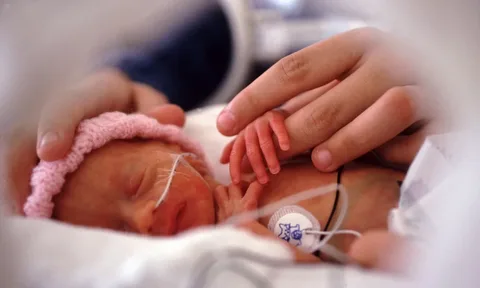
Retinopathy of Prematurity
Around 24% of childhood blindness in India is due to retinal issues. The increasing survival of premature babies in the country has led to a significant increase in conditions like Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP), a sight-threatening ailment stemming from abnormal blood vessel development in the retina of premature infants.
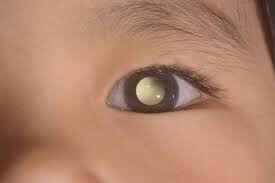
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma is a severe eye cancer primarily found in children. It originates in the retina, the inner eye layer, and is often discovered too late to prevent eye loss. As it advances, it can appear as a white mass within the eye. In later stages, if it spreads outside the eye, it becomes life-threatening.
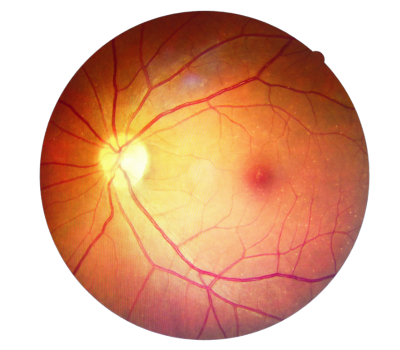
Central Serous Chorioretinopathy (CSCR)
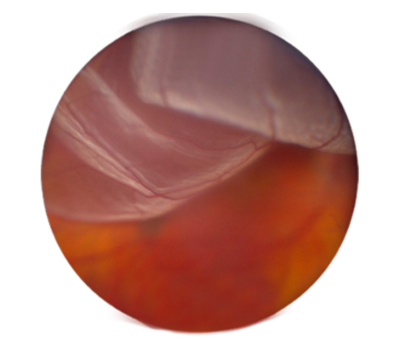
Retinal Detachment
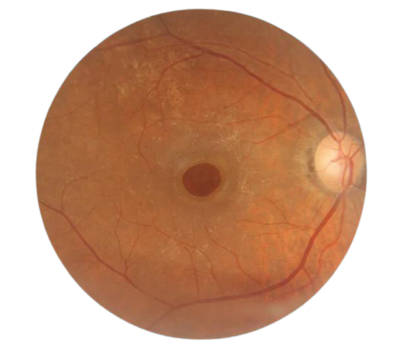
Macular Hole
Retina Technology
OPTOPOL Revo FC OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY(OCT)
- Fully automated and easy to use
- Ultra high speed
- OCT is like an ultrasonography of the retina to pick up lesions in different layers of the retina.

Optovue RTVue OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY
- Gold Standard in Epithelial mapping due to second to none accuracy and precision
- OCT is like an ultrasonography of the retina to pick up lesions in different layers of the retina.
Zeiss Visucam Fundus camera
- Captures Ultra High resolution retinal images to effectively aid in diagnosing and monitoring a broad range of eye conditions
- Extra Wide Field Retinal Images to pick up lesions in the Periphery of the retina too
- Semi Automated
- Minimal Scan Time
OPTOPOL Revo FC
OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY(OCT)
Optovue RTVue OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY
Zeiss Visucam Fundus camera

- Fully automated and easy to use
- Ultra high speed
- OCT is like an ultrasonography of the retina to pick up lesions in different layers of the retina.
- Gold Standard in Epithelial mapping due to second to none accuracy and precision
- OCT is like an ultrasonography of the retina to pick up lesions in different layers of the retina.
- Captures Ultra High resolution retinal images to effectively aid in diagnosing and monitoring a broad range of eye conditions
- Extra Wide Field Retinal Images to pick up lesions in the Periphery of the retina too
- Semi Automated
- Minimal Scan Time
Pediatric Doctor
Pediatric Patient Reviews
Karan Kothari
Tan
Sakshi Shetty
Frequently Asked Questions
Various eye issues can impact children, and there are signs that might suggest vision problems:
Indicators of poor vision in a child include:
- Sitting too close to the TV.
- Struggling to read from the blackboard or making errors when copying from it.
- Frequently stumbling or tripping over objects.
- Holding books very close to the face.
- Squinting or eyes crossing.
- Using an unusual head or face position, like looking from the sides.
- Eyes shaking.
- Itching or rubbing of the eyes.
- Eye discharge.
- Redness in the eyes.
- Light sensitivity.
- Bulging eyes.
- White reflection in the eye’s center, which might signal serious conditions like cataract or retinal problems.
Any of these symptoms from your child should not be ignored. Some eye issues can run in families and affect your child too. Seek prompt consultation with your child’s doctor or an eye specialist for early detection and treatment of eye problems.
By the age of one, a child’s brain is about 90% developed in terms of structure. However, functional brain development remains an ongoing process that relies on learning and information absorption. Similarly, a child’s eyes and the connections between the eyes and the brain are also in a developing stage. This growth and maturation can be disrupted by poor vision, potentially leading to a condition called lazy eye or amblyopia. Lazy eye occurs when one eye, or less commonly both, fails to achieve its full visual potential. Failing to address the underlying cause of lazy eye in a timely manner can result in permanent vision loss. Unfortunately, correcting the cause later in life cannot restore vision in the affected eye.
The causes of lazy eye include:
- Squint (crossed eyes)
- Uneven refractive error
- High uncorrected refractive error in both eyes (hyperopia, myopia, or astigmatism)
- Cataract
- Corneal opacity
- Eyelid drooping
- Congenital or genetic eye conditions like coloboma (structural eye defect), lens dislocation (ectopialentis), and drooping eyelid (ptosis) can occur.
- Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) affects premature infants, particularly those with low birth weight, septicemia, infections, and extended ventilation. ROP can lead to blindness if not promptly detected and treated.
- Congenital cataracts, which can be hereditary or caused by infections, trauma, or medications, are another concern.
- Cortical visual impairment (CVI) results from brain’s visual area damage, usually during neonatal stage.
- Certain childhood cancers like retinoblastoma are possible.
- Children with specific systemic conditions such as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile diabetes, meningitis, nephrotic syndrome, and metabolic disorders might face elevated risks of developing certain eye problems.
- Correcting refractive errors.
- Addressing squint using glasses.
- Performing squint surgery for children and adults.
- Pediatric cataract surgery.
- Procedures like membranectomy and YAG capsulotomy (for posterior capsular opacification).
- Implanting secondary IOLs for aphakic children.
- Conducting prism trials and prismatic correction for double vision.
- Treating amblyopia both at home and in the clinic.
- Offering binocular vision clinic orthoptics exercises.









